Your continued
donations keep Wikipedia running!
Commutativity of conjunction
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In logic, the commutativity of conjuction demonstrates that predicates on both sides of a logical conjunction operator are interchangeable. This logical law is a part of classical logic.
For any two or more propositons H1, H2, ... Hn, it is the case that:
- H1
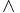 H2
H2 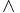 ...
... 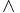 Hn
Hn
is equivalent to
- Hn
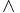 ...
... 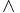 H2
H2 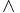 H1
H1
For example, if H1 is
- It is raining
H2 is
- Socrates is mortal
and H3 is
- 2+3=5
then
It is raining and Socrates is mortal and 2+3=5
is equivalent to
Socrates is mortal and 2+3=5 and it is raining
and the other orderings of the predicates.

