EXPONENTIALS
ANIL MITRA PHD, COPYRIGHT © 2000, REFORMATTED June 25, 2003
EXPONENTIALS
1. Rules
XA+B = XA . XB
XAB = (XA)B = (XB)A
Common values for the exponent X
are e and 10. e, the base of “natural logarithms” is
useful - especially in higher mathematics.
2. Examples
|
103 = 10x10x10 |
ex
= lim n®0 [1+x/m]m |
|
|
|
101 = 10 |
e
= 2.71828 |
|
|
|
100 = 1 |
e0
= 1 |
X0
= 1 if X ¹
0 |
|
|
10-3 = 1/103 |
|
|
|
Fractions
100.5 = 10(1/2)
= z ® z2
= (101/2)2 = 10
or, 100.5
= 10(1/2) = 2Ö10
similarly
X0.6 = 10ÖX6
Any number
X7.6 = X7+0.6
= X7 .
X0.6
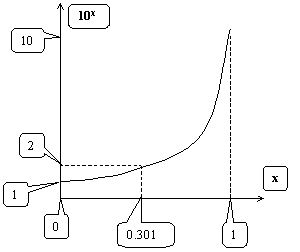
3. A
graph
ANIL MITRA | RESUME | HORIZONS ENTERPRISES™ | HOME | SITE-MAP | USEFUL
LINKS | CONTACT
PHILOSOPHY OF MIND